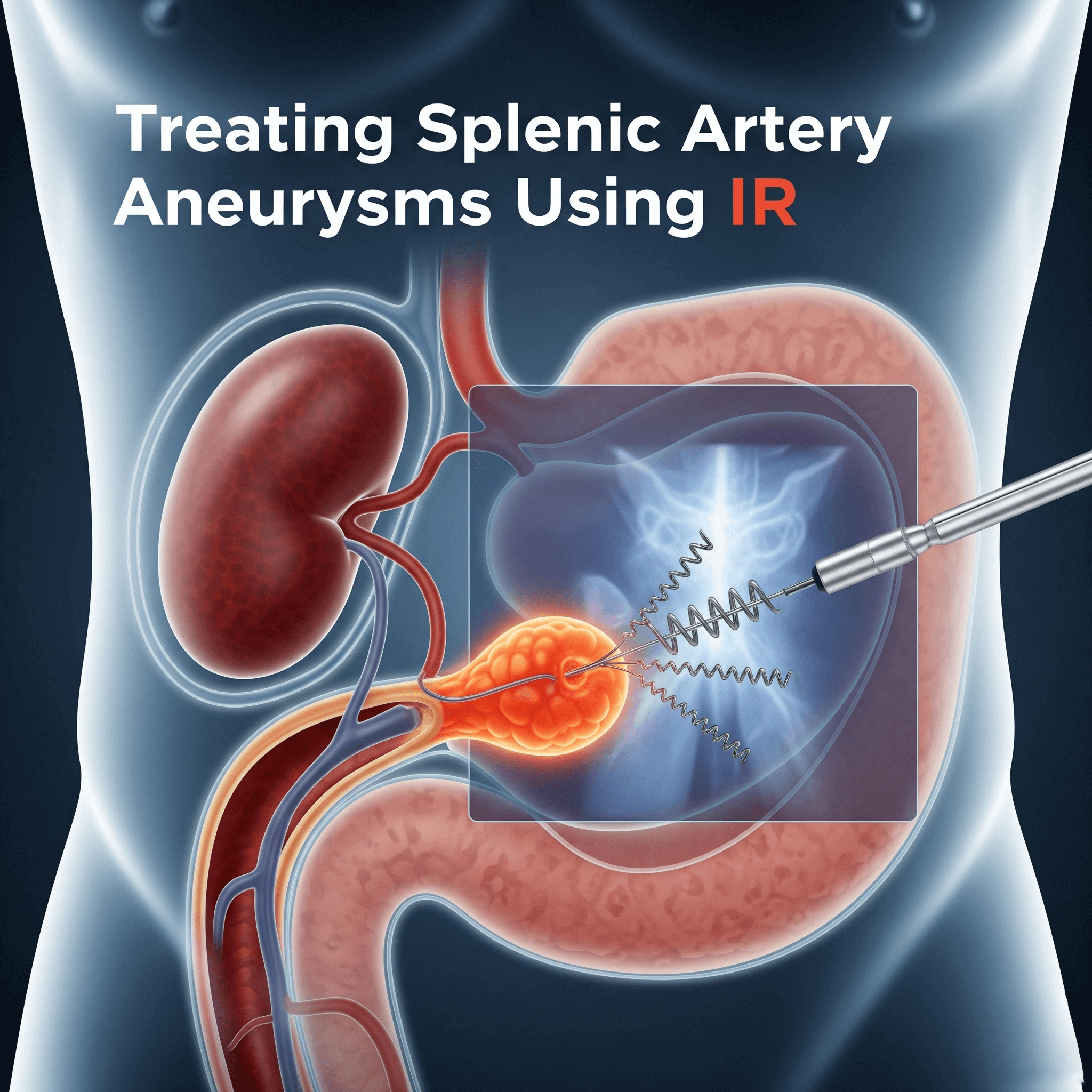
Treating Splenic Artery Aneurysms Using IR
Introduction
Splenic artery aneurysm treatment plays a crucial role because this rare vascular condition can become life-threatening if it ruptures. In the past, open surgery was the only option, and patients faced long recovery times with higher risks. Today, however, interventional radiology (IR) has changed the way doctors manage this condition. As a result, modern splenic artery aneurysm treatment is safer, minimally invasive, and ensures faster recovery.
At Dr. Vrishit Saraswat patients receive state-of-the-art, personalized care tailored to their unique health needs.
What Is a Splenic Artery Aneurysm?
A splenic artery aneurysm forms when the wall of the splenic artery weakens and bulges outward. In many cases, patients experience no symptoms, and doctors often detect it incidentally during imaging tests. However, when the aneurysm enlarges, it can cause abdominal pain or rupture, which may lead to internal bleeding.
For example, risk factors such as pregnancy, liver disease, and high blood pressure increase the likelihood of developing this condition. You can read more about splenic artery aneurysm.
Modern Splenic Artery Aneurysm Treatment Options
Thanks to advances in medicine, doctors now prefer minimally invasive methods over traditional open surgery.
1. Splenic Artery Aneurysm Embolization
Doctors most often use embolization as the primary splenic artery aneurysm treatment. During this procedure, they guide a catheter through the artery and place tiny coils or plugs to block blood flow to the aneurysm. As a result, the aneurysm seals off and the risk of rupture decreases.
2. Endovascular Stent Graft Placement
In certain cases, doctors use stent grafts to reinforce the weakened artery wall. This approach allows normal blood flow to continue while isolating the aneurysm. Furthermore, it helps preserve the function of the spleen.
3. Other IR Approaches
Specialists sometimes use liquid embolics or covered stents, depending on the patient’s specific condition. In addition, IR techniques are customizable, ensuring that each patient receives the safest option.
Benefits of Splenic Artery Aneurysm Treatment
Compared to open surgery, splenic artery aneurysm treatment with endovascular methods provides many advantages:
- Shorter recovery time – patients often return home within a day or two.
- Less pain – small incisions reduce discomfort.
- Lower risk – minimally invasive methods reduce complications.
- Kidney and spleen preservation – important organs remain functional.
- High success rate – durable and effective results.
Therefore, patients enjoy a better quality of life after treatment.
Recovery After Splenic Artery Aneurysm Treatment
Recovery is usually smooth. Most patients resume normal activities within a week. On the other hand, heavy exercise and strenuous tasks should wait until the doctor provides clearance. Follow-up imaging ensures the aneurysm remains sealed and the artery continues to function well.
At Dr. Vrishit Saraswat patients benefit from careful post-treatment monitoring and ongoing support.
Conclusion & Call to Action
In summary, splenic artery aneurysm treatment has advanced significantly with the help of interventional radiology. Embolization, stent grafting, and other endovascular techniques now replace open surgery in most cases. Finally, patients can expect safer outcomes, quicker recovery, and improved overall health.
If you or a loved one has been diagnosed with a splenic artery aneurysm, do not delay. Book a consultation with Dr. Vrishit Saraswat today and explore the safest, most advanced treatment options for your condition.
FAQs
Q1: What is the treatment for splenic artery aneurysm?
Most splenic artery aneurysms can now be treated using minimally invasive interventional radiology techniques.
- Endovascular embolization (blocking blood flow with tiny coils or plugs)
- Covered stent-graft placement (to seal the aneurysm while keeping blood flow normal)
These are done through a small pinhole in the groin or wrist, without open surgery. In rare cases, traditional surgery (ligation, resection, or splenectomy) may be needed.
Q2: What size splenic artery aneurysm is treated?
Treatment is generally recommended if the aneurysm is:
- Larger than 2 cm
- Growing in size
- Symptomatic (causing pain or discomfort)
- In women of childbearing age or during pregnancy (higher rupture risk)
- Ruptured or at risk of rupture
Early treatment with endovascular methods can prevent life-threatening complications.
Q3: What specialist treats splenic artery aneurysm?
Splenic artery aneurysms are best managed by Interventional Radiologists—specialists trained in performing image-guided, minimally invasive vascular procedures. They use advanced imaging (like angiography, CT, ultrasound) to precisely treat the aneurysm without major surgery.