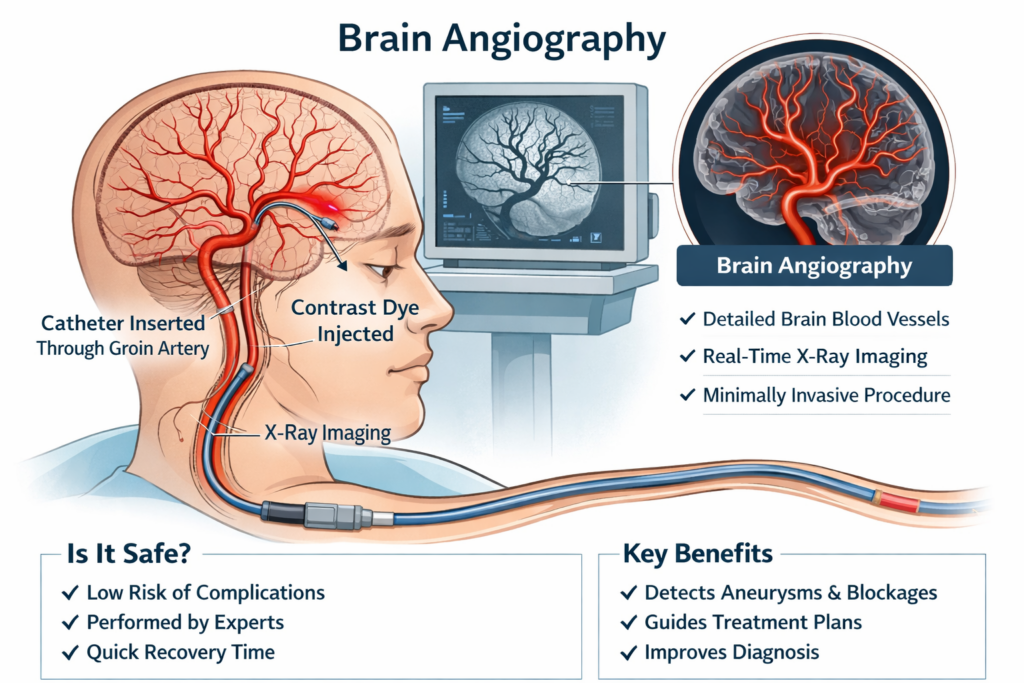
Understanding medical procedures can feel overwhelming—especially when the word “brain” is involved. If your doctor has recommended brain angiography, it’s completely natural to ask: Is it safe? What happens during the test? Will it hurt?
You’re not alone. Many patients search for clear, trustworthy, and easy-to-understand information before agreeing to this diagnostic procedure. In this detailed guide, we will walk you through everything you need to know about brain angiography (also called cerebral angiography)—from safety and preparation to benefits, risks, and recovery. Let’s break it down in a simple, human way—without fear, jargon, or confusion
What Is Brain Angiography?
Brain angiography, or cerebral angiography, is a medical imaging test used to visualize the blood vessels in the brain.
It helps doctors identify issues such as:
– Blocked or narrowed arteries
– Brain aneurysms
– Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs)
– Stroke-related problems
– Tumors affecting blood flow
Think of it as a high-definition map of your brain’s blood vessels. Instead of roads and traffic, doctors look at arteries and blood flow.
Why Do Doctors Recommend This Test?
Doctors recommend brain angiography when other imaging tests, like CT or MRI scans, don’t provide enough clarity.
Common reasons include:
– Sudden severe headaches
– Suspected brain aneurysm
– Unexplained stroke or mini-stroke (TIA)
– Abnormal findings on CT or MRI
– Pre-surgical planning
– Monitoring known vascular conditions
It allows physicians to see precise blood flow patterns, which helps them make critical decisions.
How Does the Procedure Work?
Brain angiography uses contrast dye and X-ray imaging to highlight blood vessels in real time.
Step-by-Step Overview:
1. A small catheter is inserted, usually through the wrist or groin.
2. The catheter is gently guided to the arteries supplying the brain.
3. A contrast dye is injected.
4. Advanced imaging captures detailed vascular images.
5. The catheter is removed, and pressure is applied to prevent bleeding.
The entire process usually takes 30 to 60 minutes.
Is Brain Angiography Safe?
Yes, brain angiography is generally very safe, especially when performed by skilled interventional radiologists.
Modern technology and strict safety measures have greatly reduced risks. Serious complications are rare, occurring in less than 1% of cases.
Why It’s Considered Safe ?
– Minimally invasive technique
– Performed under local anesthesia
– Real-time imaging ensures accuracy
– Continuous monitoring during the procedure
– Most patients return home the same day
What Are the Possible Risks?
While rare, it’s important to know potential risks.
Possible Side Effects:
– Mild bruising at the catheter site
– Temporary headache
– Mild allergic reaction to contrast dye
Rare Complications:
– Stroke (very rare)
– Vessel injury
– Infection
Your doctor will carefully review your medical history to minimize risks.
Who Should Avoid Brain Angiography?
Brain angiography may not be suitable for everyone. Caution is advised if you have:
– Severe kidney disease
– Allergy to contrast dye
– Uncontrolled bleeding disorders
– Pregnancy (unless necessary)
Your doctor will weigh the benefits against potential risks.
How to Prepare for the Test?
Preparation is simple but important.
Before the Test:
– Avoid eating or drinking for 6 to 8 hours before the procedure.
– Inform your doctor about medications.
– Share any history of allergies. – Arrange for someone to take you home.
What to Wear:
– Comfortable clothing
– Avoid jewelry or metal objects
What Happens During the Procedure?
You’ll stay awake but relaxed. A local anesthetic will keep you comfortable.
What You May Feel:
– Mild warmth during dye injection
– Slight pressure at the catheter site
Most patients find the experience uncomfortable but not painful.
What Happens After the Test?
After the procedure:
– You’ll rest for a few hours.
– Your vital signs will be monitored.
– You may be advised to drink fluids.
Recovery Time Most patients return to normal activities within 24 hours.
Brain Angiography vs Other Imaging Tests
| Test | Best For | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| CT Scan | Quick imaging | Less detail |
| MRI | Soft tissue imaging | Not ideal for blood flow |
| Brain Angiography | Detailed vascular mapping | Invasive but precise |
Brain angiography remains the gold standard for vascular diagnosis.
Benefits of Brain Angiography
– High diagnostic accuracy
– Early detection of serious conditions
– Enables minimally invasive treatment planning
Who Performs Brain Angiography?
A trained interventional radiologist—a doctor specialized in image-guided treatments—performs the procedure. Their expertise lowers risks and improves results.
How Long Do Results Take?
Results are often reviewed immediately, with a detailed report available within 24 to 48 hours.
When Should You Contact Your Doctor After the Test?
Call your doctor if you notice:
– Severe pain
– Persistent bleeding
– Fever
– Numbness or weakness
These are rare but should be addressed promptly.
Is Brain Angiography Worth It?
If your doctor has recommended it, the answer is usually yes.
The clarity it provides can:
– Save time
– Prevent complications
– Enable early treatment
In many cases, it can be life-saving.
Conclusion
Brain angiography is a safe, precise, and effective diagnostic tool that helps doctors understand complex conditions related to brain blood vessels. With modern technology and skilled specialists, risks are minimal, and benefits are substantial. If your doctor has suggested this test, you can feel confident knowing it plays a crucial role in accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
No. Most patients experience only mild discomfort during catheter insertion.
Usually 24 hours or less.
No, fasting for 6 to 8 hours is usually required.
For blood vessel imaging, yes—it provides more detailed results.
The radiation exposure is minimal and within safe medical limits.