Introduction: A New Hope for Men With Enlarged Prostate
An enlarged prostate is a common yet often ignored condition affecting millions of men, especially after the age of 50. Many men silently live with frequent urination, interrupted sleep, and discomfort, believing surgery is the only solution. Today, medical innovation has changed that narrative. Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) has emerged as a breakthrough, non-surgical treatment offering effective relief with faster recovery and fewer risks.
What Is an Enlarged Prostate (Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia – BPH)?
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland. As the prostate grows, it presses against the urethra, disrupting normal urine flow. This condition is not cancer, but its symptoms can significantly impact quality of life if left untreated.
Common Symptoms of Enlarged Prostate
Men with BPH may experience:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Weak or interrupted urine stream
- Difficulty starting urination
- Sudden urgency to urinate
- Incomplete bladder emptying
These symptoms often worsen gradually, making early diagnosis and treatment essential.
How BPH Impacts Quality of Life
Chronic sleep disruption, anxiety about bathroom access, and reduced confidence can affect personal, social, and professional life. Many men avoid travel or social gatherings due to fear of urinary urgency. Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) directly addresses these concerns by targeting the root cause.
Traditional Treatment Options for Enlarged Prostate
Initial treatment often includes lifestyle changes or medications aimed at relaxing prostate muscles or shrinking the gland. While medications may help temporarily, they often come with side effects such as dizziness, fatigue, or sexual dysfunction.
Surgical Treatments: What Are the Downsides?
Traditional prostate surgeries may require hospitalization, general anesthesia, and weeks of recovery. Risks can include bleeding, urinary incontinence, and sexual side effects. These concerns have led many patients to seek safer alternatives like Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE).
The Breakthrough: Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE)
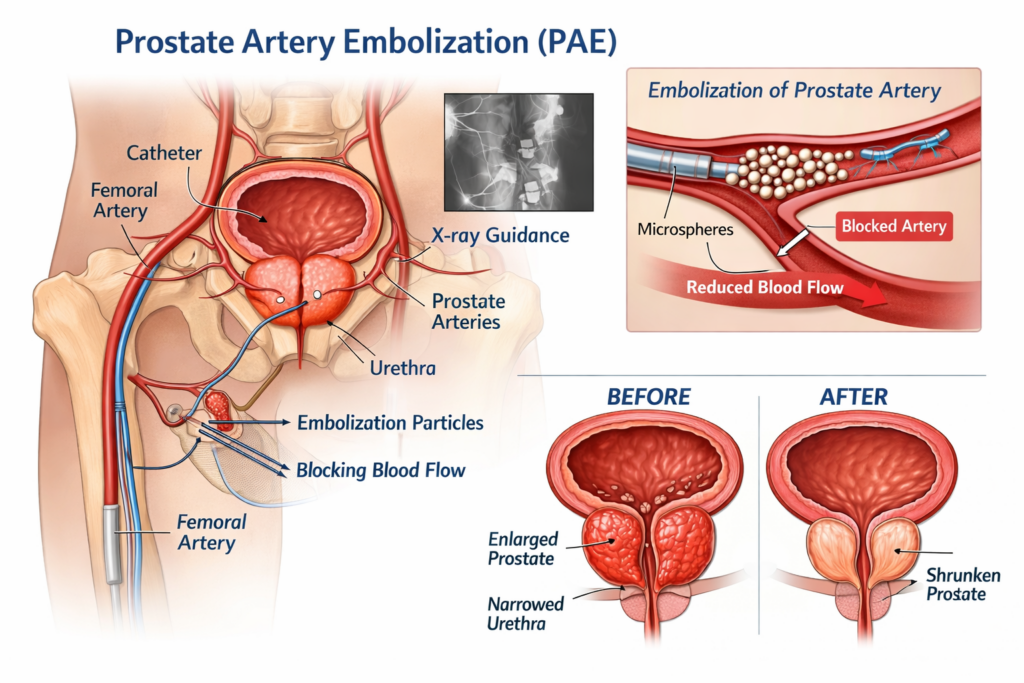
Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) is a minimally invasive, image-guided procedure performed by an Interventional Radiology specialist. Instead of removing prostate tissue surgically, PAE reduces blood flow to the prostate, causing it to gradually shrink and relieve symptoms.
What Makes PAE a Breakthrough?
- No surgical cuts or stitches
- No removal of prostate tissue
- Performed under local anesthesia
- Preserves urinary and sexual function
- Faster recovery compared to surgery
PAE represents a shift toward organ-preserving, patient-centered care.
How Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) Works
The procedure begins with detailed imaging to map the prostate’s blood supply. A thin catheter is inserted through a small puncture in the wrist or groin and guided to the prostate arteries. Tiny medical particles are released to block excessive blood flow.
As blood supply reduces, the prostate gradually shrinks, easing pressure on the urethra and improving urinary flow.
Procedure Duration and Comfort
- Typically lasts 1–2 hours
- Performed under local anesthesia
- Minimal discomfort
- Most patients return home the same day
Benefits of Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE)
PAE offers multiple advantages over conventional treatments:
- Significant symptom relief
- Minimal pain and complications
- Quick return to daily activities
- No hospital stay in most cases
PAE vs Surgery: A Comparison
| Factor | PAE | Surgery |
| Invasiveness | Minimally invasive | Highly invasive |
| Recovery | Few days | Weeks |
| Anesthesia | Local | General |
| Sexual side effects | Rare | Possible |
Who Is an Ideal Candidate for PAE?
Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) is ideal for:
- Men with moderate to severe BPH symptoms
- Patients who want to avoid surgery
- Men with other medical conditions making surgery risky
- Patients concerned about sexual side effects
Who May Not Be Suitable?
Not all patients are ideal candidates. Certain prostate anatomy or other urological conditions may require alternative treatments. A thorough evaluation by a specialist is essential.
Recovery and Post-PAE Expectations
Most patients experience mild discomfort for a few days, manageable with medication. Urinary symptoms may begin improving within weeks, with continued improvement over several months.
Patients can typically:
- Resume normal activities in 1–2 days
- Avoid heavy exertion briefly
- Follow simple post-procedure care instructions
Safety, Effectiveness, and Clinical Outcomes
Clinical studies worldwide show Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) to be a safe and effective treatment for BPH. It delivers durable symptom relief with a low complication rate and high patient satisfaction.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is PAE painful?
No. Most patients report mild discomfort only.
How soon will I see results?
Symptom improvement typically begins within weeks.
Will PAE affect sexual function?
PAE is designed to preserve sexual and urinary function.
Is PAE permanent?
PAE provides long-term relief for most patients, with ongoing benefits.
Why Men Are Choosing Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE)
Men today are better informed and actively seeking treatments that prioritize safety, recovery, and quality of life. Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) aligns perfectly with this shift toward minimally invasive medicine.
When to Consult a Specialist
If urinary symptoms interfere with daily life, early consultation is crucial. Timely evaluation allows access to advanced options like Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) before complications arise.
Conclusion: A Smarter, Safer Way to Treat Enlarged Prostate
An enlarged prostate no longer means inevitable surgery. Prostate Artery Embolization (PAE) offers men a modern, effective, and minimally invasive path to relief—without the risks of traditional surgery. Informed decisions lead to better outcomes, and PAE represents the future of prostate care