A New Era of Life-Saving Treatment
Medical science has evolved rapidly, offering safer and less invasive treatment options for complex conditions. One such breakthrough is the angioembolization procedure, a minimally invasive technique that can control bleeding, treat tumors, and manage vascular conditions—often without the need for open surgery.
For many patients who are not ideal candidates for traditional surgery, the angioembolization procedure provides a safer, faster, and highly effective alternative. It reduces recovery time, minimizes pain, and lowers the risk of complications while delivering excellent clinical outcomes.
What Is Angioembolization?
The angioembolization procedure is a minimally invasive treatment performed by an Interventional Radiologist. It involves intentionally blocking specific blood vessels to stop abnormal blood flow or shrink abnormal tissue, such as tumors or fibroids.
Using advanced imaging techniques, such as fluoroscopy or CT guidance, the doctor navigates a tiny catheter through the blood vessels to the targeted area. Small embolic materials—such as particles, coils, or medical glue—are then released to block blood flow precisely where needed, without affecting surrounding healthy tissue.
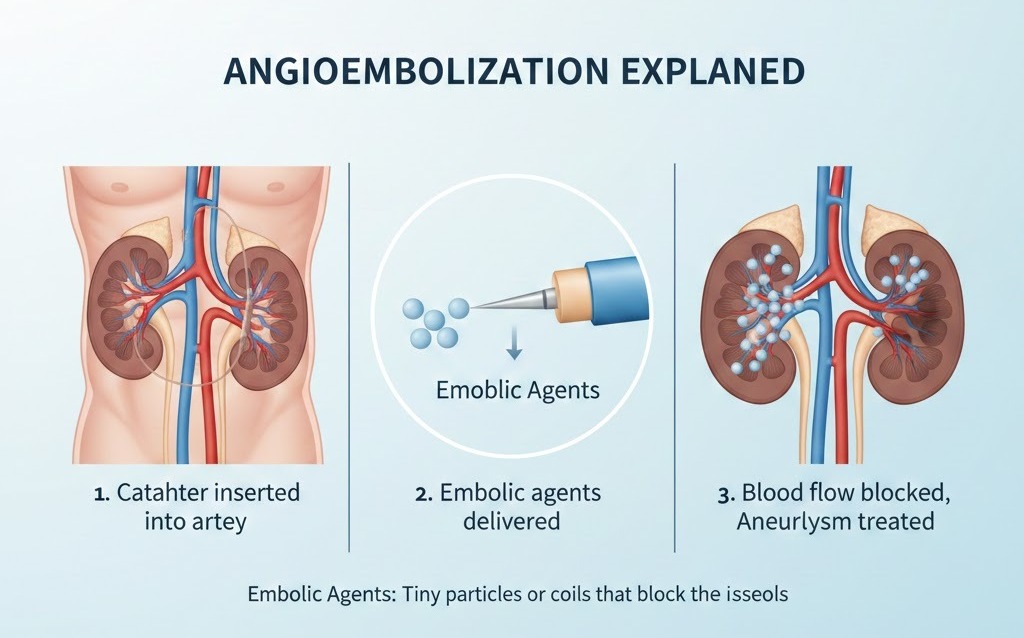
How the Angioembolization Procedure Works (Step by Step)
The angioembolization procedure is carefully planned and executed in a controlled medical environment:
Step 1: Accessing the Blood Vessel
A tiny puncture is made, usually in the wrist or groin. No large incision is required.
Step 2: Catheter Navigation
A thin, flexible catheter is guided through the blood vessels using real-time imaging.
Step 3: Targeted Embolization
Special embolic agents are released to block the abnormal blood supply.
Step 4: Confirmation
Imaging confirms successful blockage and restoration of normal blood flow patterns.
This precision ensures that only the affected area is treated, preserving healthy surrounding tissues.
Conditions Treated with Angioembolization
The angioembolization procedure is used in a wide range of medical conditions, including:
- Uncontrolled internal bleeding (due to trauma or injury)
- Uterine fibroids (Uterine Artery Embolization)
- Liver tumors and cancers
- Benign prostate enlargement (BPH)
- Vascular malformations and aneurysms
- Varicose veins and pelvic congestion syndrome
Its versatility makes it one of the most powerful tools in modern interventional medicine.
Why Angioembolization Is a Safer Alternative to Surgery
Compared to traditional surgery, the angioembolization procedure offers several advantages:
- No large incisions or stitches
- Minimal blood loss
- Lower risk of infection
- Reduced hospital stay
- Faster recovery and return to daily activities.
- Often performed under local anesthesia.
These benefits make it especially suitable for elderly patients or those with medical conditions that make surgery risky.
What to Expect Before, During, and After the Procedure
Before the Procedure
- Medical evaluation and imaging tests
- Blood test, ts if required
- Short hospital admission
During the Procedure
- Usually lasts 30–90 minutes.
- Mild discomfort but no major pain
- Patient remains awake in most cases.
After the Procedure
- Short observation period
- Mild soreness at the access site
- Most patients go home the same day or the next day.
Recovery and Results
Recovery after an angioembolization procedure is typically quick. Most patients return to normal activities within a few days. Improvement in symptoms may begin within days or gradually over weeks, depending on the condition treated.
Follow-up imaging is sometimes recommended to ensure long-term success and stability.
Is the Angioembolization Procedure Right for You?
The procedure is ideal for patients who:
- Want to avoid open surgery
- Have medical conditions that increase surgical risk
- Need a targeted, organ-preserving treatment.t
However, every patient is different. A consultation with an experienced Interventional Radiologist is essential to determine suitability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Most patients experience minimal discomfort, which is managed easily with medication.
In many cases, yes. Some conditions may require follow-up treatment depending on disease progression.
Complications are rare but may include mild pain, temporary fever, or minor bruising.
Success rates are high when performed by experienced specialists using modern imaging technology.
Final Thoughts: A Life-Saving Innovation
The angioembolization procedure represents a major advancement in modern medicine. By offering a safe, effective, and minimally invasive alternative to surgery, it has transformed treatment outcomes for countless patients worldwide.
If you or a loved one is exploring treatment options, consulting an experienced Interventional Radiologist could be the first step toward faster recovery and improved quality of life.